SmartHands aims to implement digital media in professional education and training for the health professions.
1
2
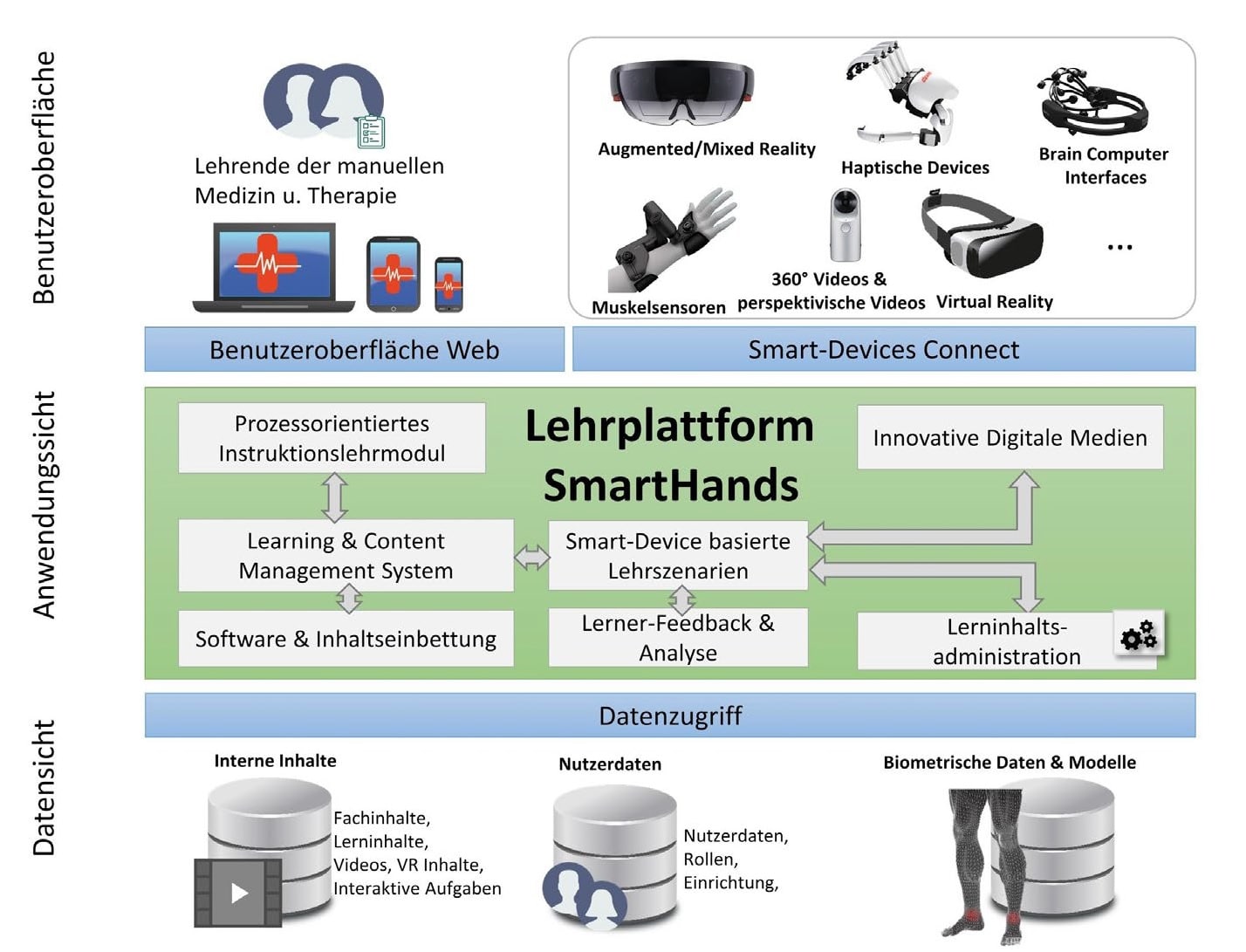
Teaching scenarios for digital media use in the domain of manual medicine and therapy are developed and integrated into a learning platform
3
With innovative technologies such as mixed reality glasses, smart wearables, haptic and brain-machine interfaces, the diverse innovative application possibilities of SmartHands are made possible.
Principal Investigator

Dr. Dirk Werth
managing director and
scientific director

Contact Person

dr Florian Beier
E-Mail: florian.beier@aws-institut.de
Mobilephone: + 49 681 93511 318
Short & to the point
What?
These problems are addressed in the project with a teaching platform which, as an eLearning web solution, depicts three innovative pilot teaching scenarios and thus trains training and further education staff in the use of smart-device-based media. The constructed platform will be modularly expandable with further smart-device-based teaching scenarios. The optimal transfer of specialist knowledge and efficient use in subsequent learning scenarios are evaluated and researched.
How?
Because both the theoretical learning of real medical cases, as well as the traditional learning on dummies or simulated patients, does not correspond to reality and therefore only partially imparts the necessary practical skills. An improvement in teaching through digital media can therefore be expected, which can be more immersive and closer to real scenarios and can depict them completely. In particular, haptics and visual reactions of the simulated patients are fields in which such potentials are currently unfolding using new smart-device-based media.
Initial Situation
The high demand for specialists in manual medicine leads to a high need for training of the training and further education staff, which also creates opportunities for the digitalization of the specialist area. However, there are no validated teaching scenarios for the integration of digital media into existing learning and examination formats that inform teachers about the possibilities and explanations of technical use cases.
So far, there have been no exact specifications in manual medicine and therapy teaching with regard to diagnostic and therapeutic techniques, e.g. B. how often and with which objective should be practiced. The needs and practice-oriented orientation and the improvement of tactile and fine motor skills suffer as a result. As soon as feedback on individual learning progress is available, it can be included in order to adapt the teaching didactics individually. Only then can overall improved framework conditions for the implementation of the techniques in patient care be assumed.
health workers
5,7 million
High demand
of professionals
The August-Wilhelm Scheer Institute is developing the following basic component:
pilot scenarios. The integration of haptic learning and 360-degree videos in three different mixed reality applications is addressed. We develop the implementation of the exercise scenarios, as well as the software and the interaction of mixed reality with the eLearning platform.
interview with dr cand. rer. medical Lysann Kasprick Medical Education Expert:

